Microsoft MPI
MS-MPI runs on MS-Windows.
MPICH
MPICH runs on Linux and Mac OS. Windows was supported until version 1.4.1p1 but it has now stopped.
Open MPI
Open MPI is mainly developed for Linux, OS X, Solaris and Windows (Windows XP, Windows HPC Server 2003/2008 and Windows 7 RC). However, support for Windows has now stopped. Last stable version for Unix is version 1.6.5.
Windows users can use Open MPI implementations for Cygwin.
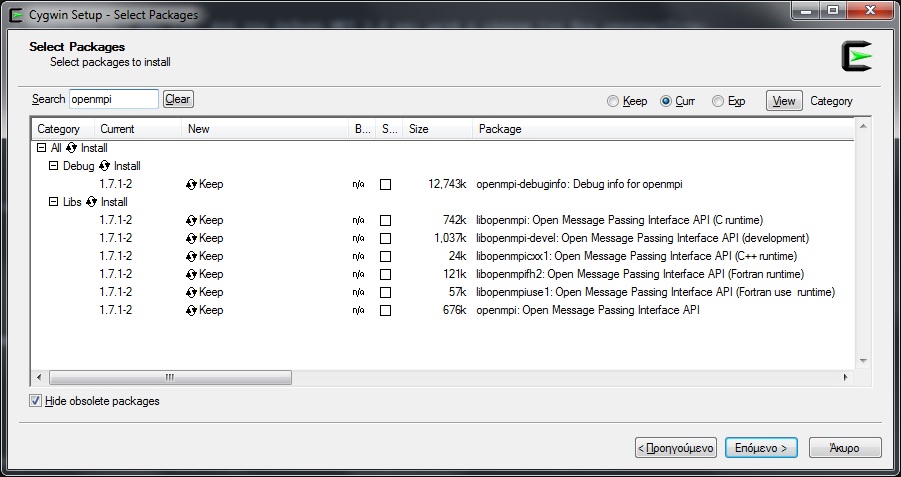
Q: I have installed MPI for Windows. What else do I need?
A:
Microsoft MPI
You need Visual Studio 2008, 2010 or 2012.
MPICH
Q: How do I write a program and compile it?
A:
Microsoft MPI
The following example is based on Visual Studio 2010.
-
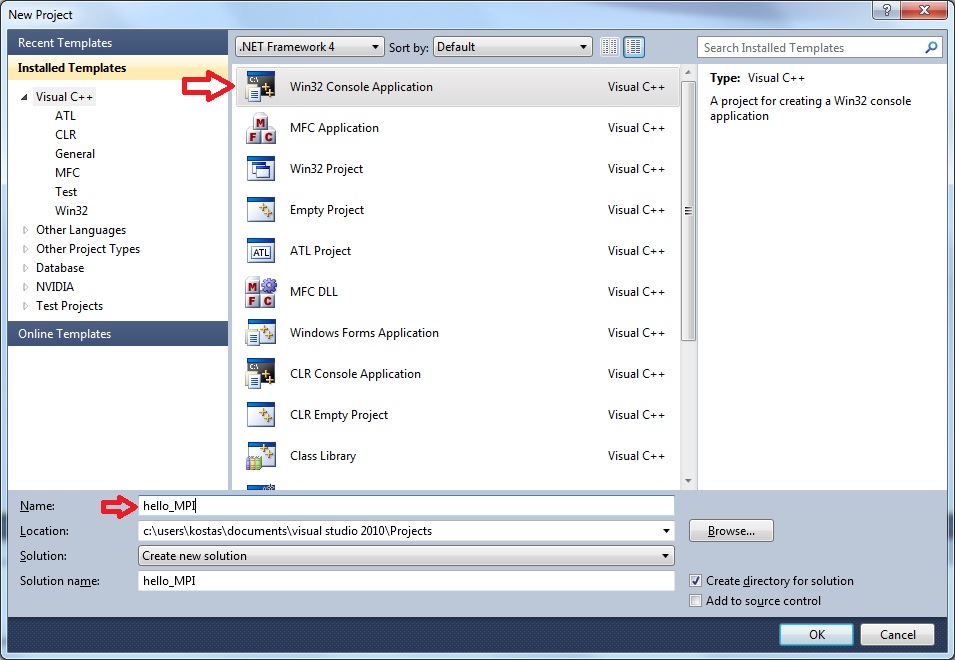
Create a new Win32 Console Application Project and give it any namme (here we caled it hello_MPI).
-
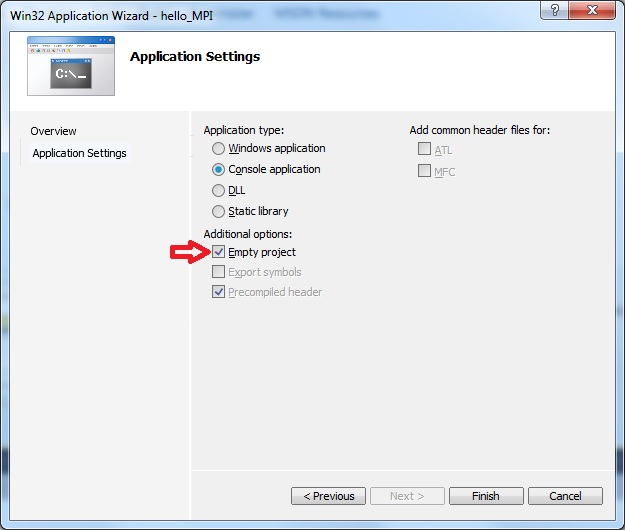
In Application Settings click on Empty Project
-
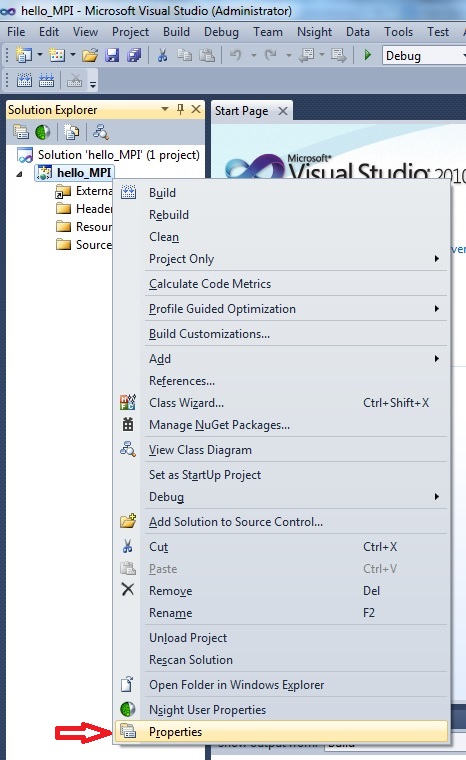
Right clicking on Project choose Properties
-
In the Configuration Properties > VC++ Directories menu add the folders Inc and Lib\i386 from the path where MS HPC Pack 2012 was installed. In our example the path is C:\Program Files\Microsoft HPC Pack 2012.
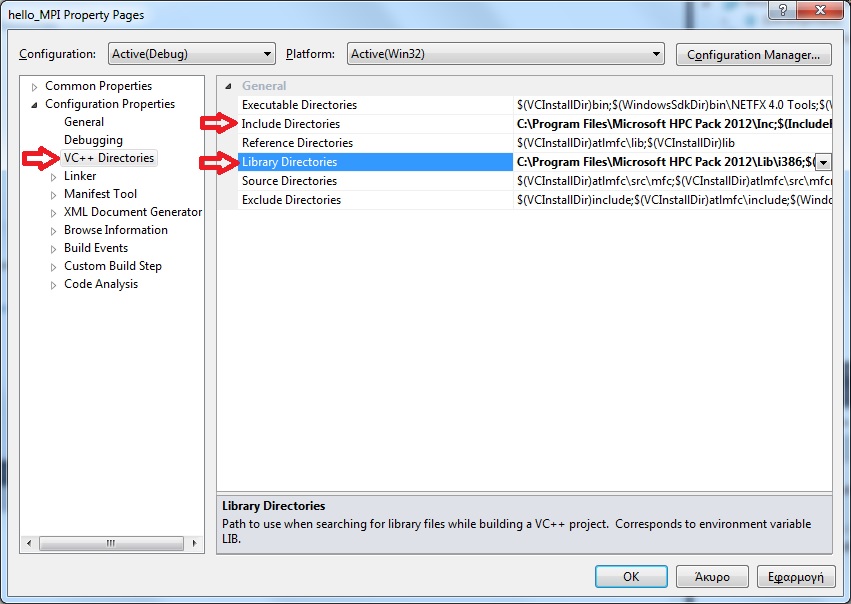
-
In the Configuration Properties > Linker > Input menu and the variable Additional Dependencies add the library msmpi.lib
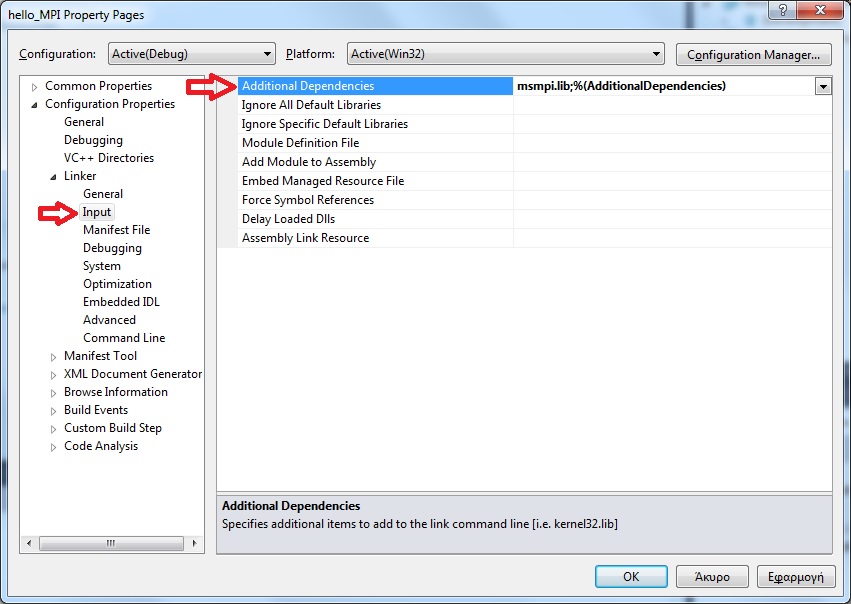
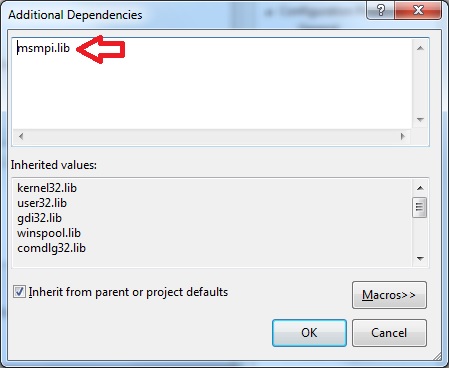
-
In the Configuration Properties > Debugging menu choose Local Windows Debugger : MPI Cluster Debugger
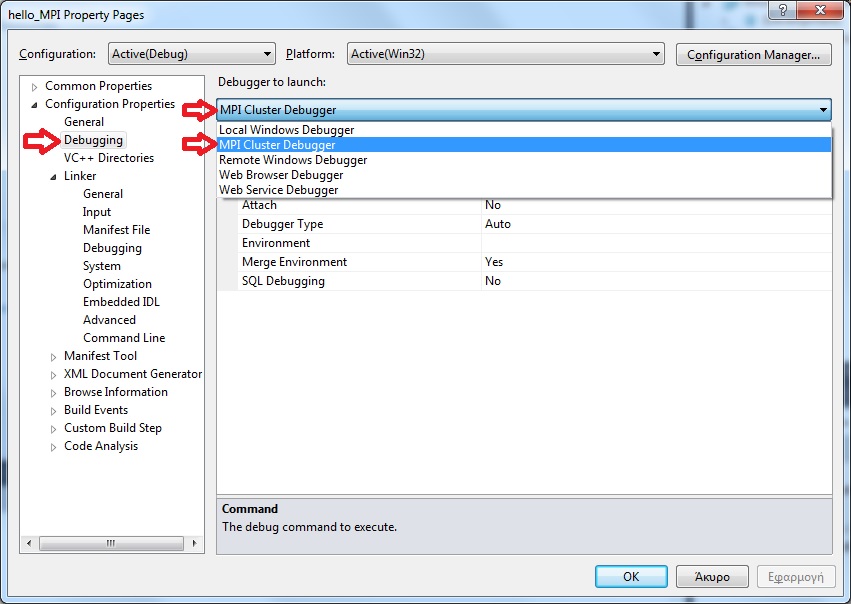
-
In case you do not have access to any cluster and simply want to run the program in your local computer, edit the variable Run Environment and in the window that pops up choose localhost and the number of concurrent processes (eg. 5).
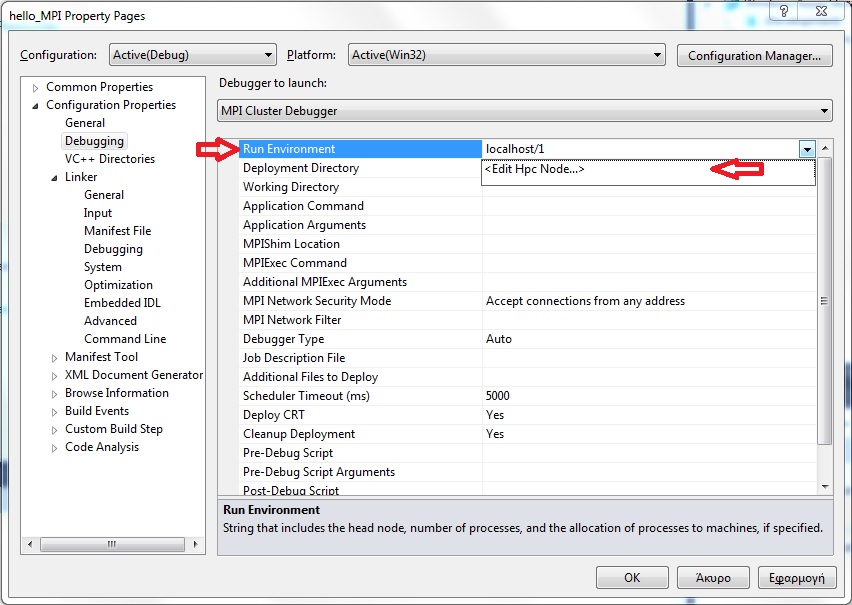
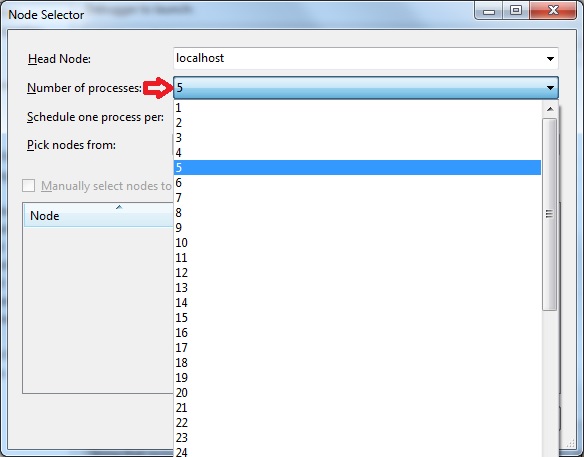
-
Then write the program adding a new C++ File in Source Files and give it the name hello_MPI.cpp.

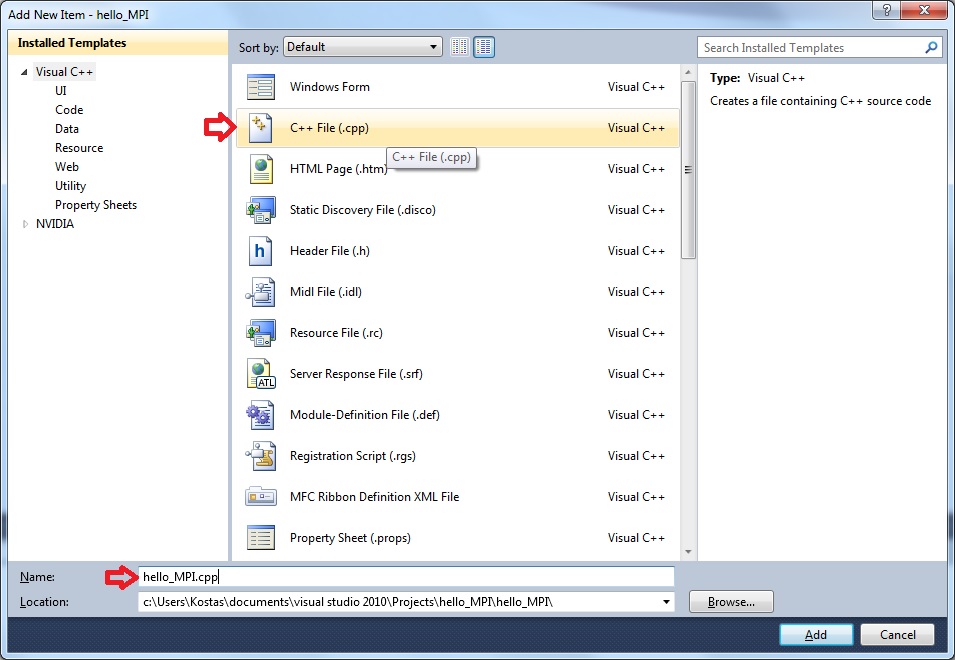
- Then click on Build and the resulting executable will be placed in the foler c:\Users\<Username>\Documents\Visual Studio 2010\Projects\hello_MPI\Debug\
MPICH
The following example uses the Eclipse IDE.
-
Create a new C project
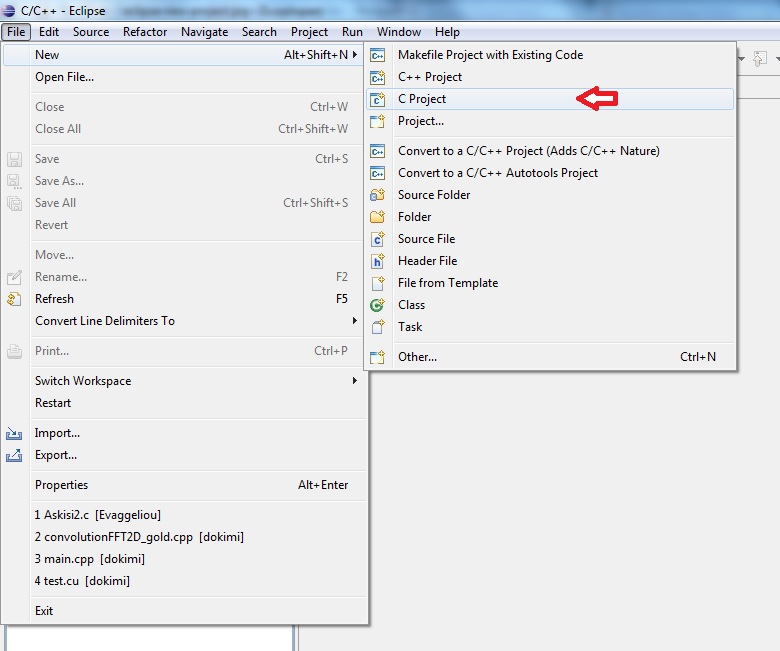
-
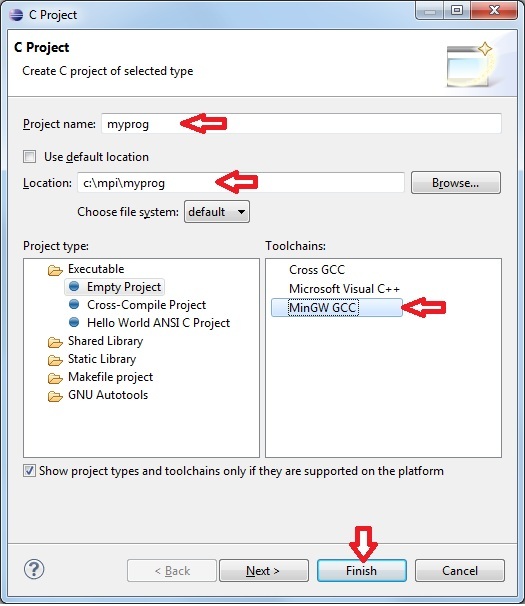
Declare the project parameters (name, path, use of MinGW compiler)
-
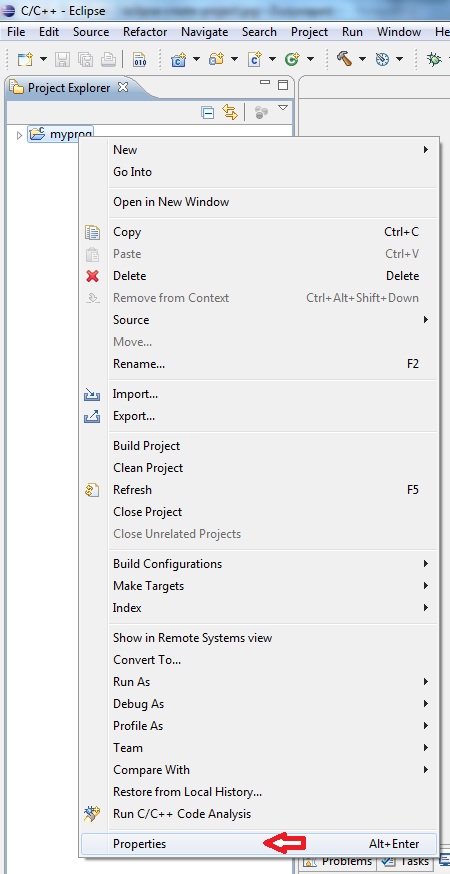
After the poject appears on the left side, right click on "Properties"
-
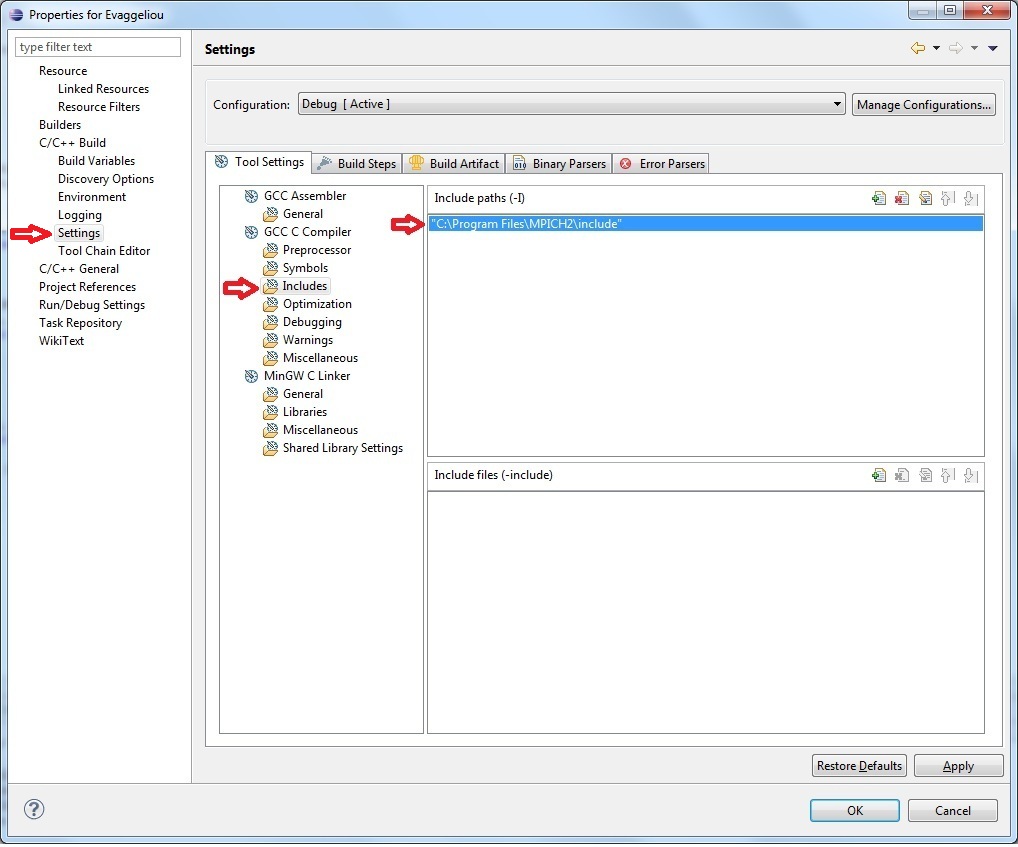
Add the include directory "C:\Program Files\MPICH2\include" in the Include paths (-I)
-
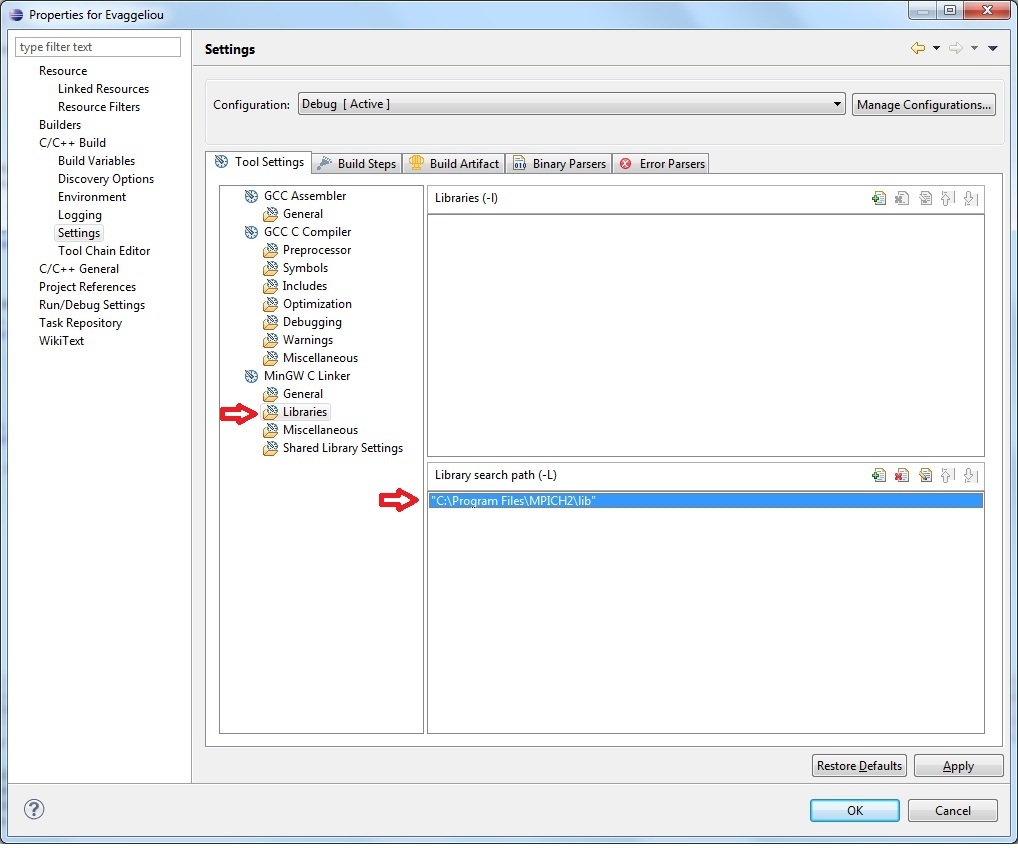
Add the library directory "C:\Program Files\MPICH2\lib" in the Library search path (-L)
-
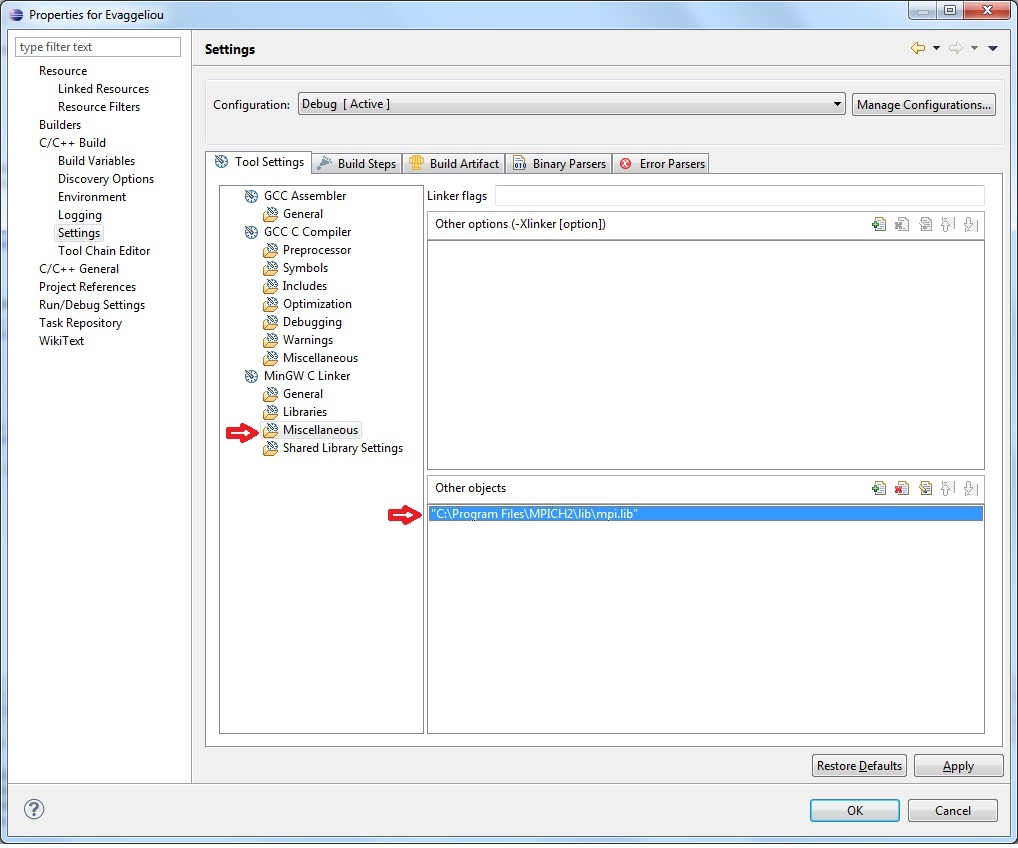
Make a link with the MPI library C:\Program Files\MPICH2\lib\mpi.lib from "Miscellaneous" > "Other objects"
-
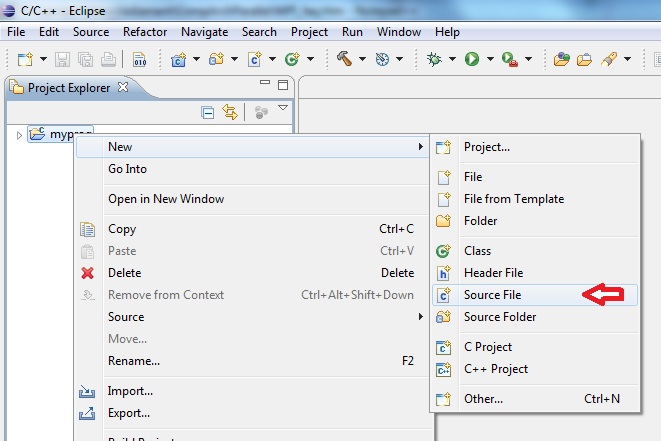
Create a new .c file and give it any name, eg. myprog.c
-
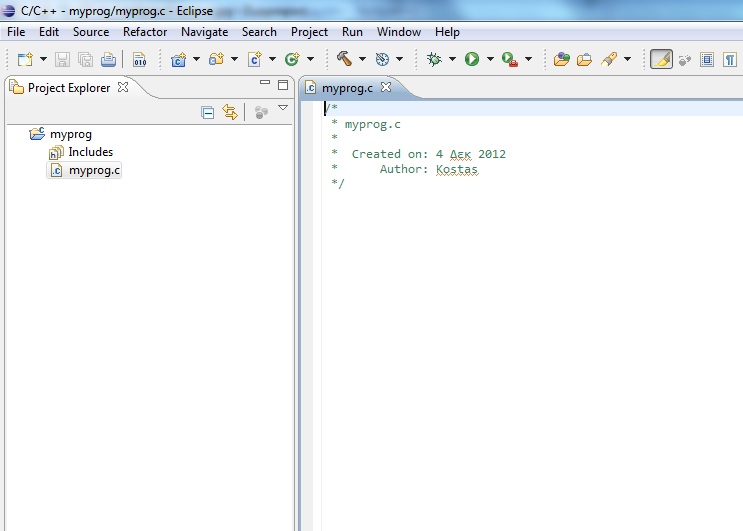
After the file myprog.c is created write the source C code in it
-
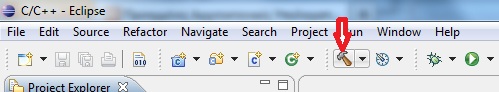
Build the program by clicking on the "hammer" icon (or by selecting the "Project" > "Build Project" menu item)
- You have now created the executable file myprog.exe in C:\mpi\myprog\Debug\.
Q: I created the executable myprog.exe. How do I run it?
A: There are various ways to run it.
- If we have access to a computer cluster then, for example, the command
mpiexec -n 8 myprog.exe
creates 8 processes which run on machines selected by the MPI deamon, from the machines available to us from the cluster.
Alternatively we can use the command
mpiexec -hosts 3 machine1 3 machine2 4 machine3 1 myprog.exe
creating a total of 8 processes running on machines machine1, machine2, and machine3. With this command we tell MPI that machine1 will execute 3 processes, machine2 will execute 4 processes and machine3 will execute 1 process. - If only a single computer is available, we can use either one of the following commands:
mpiexec -localonly 5 myprog.exe
or mpiexec -n 5 myprog.exe
Both commands will create a total of 5 processes which execute locally and can exchange messages among each other through the network loopback. This is a very useful option for debugging, especially when a cluster is not readily available.
Note: if you just run
myprog.exe
then only one process will be vreated, ie. the program will not be executed in parallel. This is equivalent to
mpiexec -n 1 myprog.exe